Data Structure in C Programming Language is a specialized format for organizing and storing data. In General data structure types include the file, array, record, table, tree.. etc.
Apart from this here we will discuss about different concepts of data structure with real time examples.
Topics to be covered:
1) Stack
2) Queue
3) linked list
4) Trees
5) Graphs


Why Tree?
Unlike Array and Linked List, which are linear data structures, tree is hierarchical (or non-linear) data structure.
Apart from this here we will discuss about different concepts of data structure with real time examples.
Topics to be covered:
1) Stack
2) Queue
3) linked list
4) Trees
5) Graphs
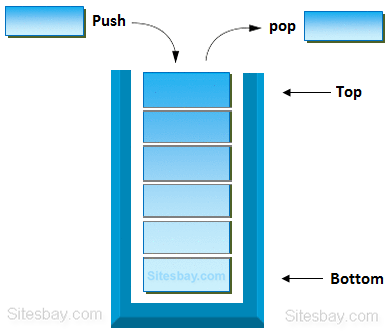
STACK
Stack is linear data structure. In stack addition of new data item and deletion of already existing data item is done from only one end, known as top. Working of stack on the basis of Last-in-First-out (LIFO) principal, it means last entered item remove first.

Working of Stack in C
A stack is a container of objects that are inserted and removed according to the Last-in First-Out (LIFO) principle. Both operation insert and deletion perform in stack only from TOP.
Real life example of stack
A most popular example of stack is plates in marriage party. Fresh plates are pushed onto to the top and popped from the top.

Stack Operation
In stack data structure mainly perform two operation; push and pop
- pop: In case of stack deletion of any item from stack is called pop.
- push: In case of stack Insertion of any item in stack is called push.
Use of stack
- Expression evaluation
- Backtracking (game playing, finding paths, exhaustive searching)
- Memory management, run-time environment for nested language features.
- To reverse a word. You push a given word to stack - letter by letter - and then pop letters from the stack.
- An "undo" mechanism in text editors; this operation is accomplished by keeping all text changes in a stack.
- space for parameters and local variables is created internally using a stack.
- compiler's syntax check for matching braces is implemented by using stack.
- Back/Forward on browsers are perform using stacks.
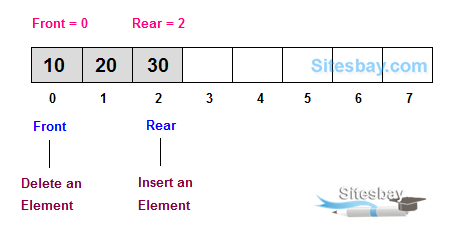
QUEUE
Queue is work on the principal of First-In-First-Out (FIFO), it means first entered item remove first. Queue have two end front and rear, from front you can insert element and from rear you can delete element.

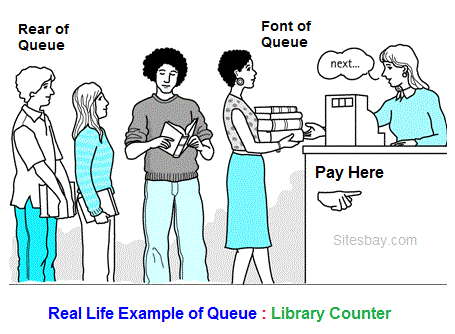
Real life example of Queue
A common example of queue is movie theater ticket counter, there first person who stand in front of ticket window take ticket first and remove from line and new person always stand in line from end.

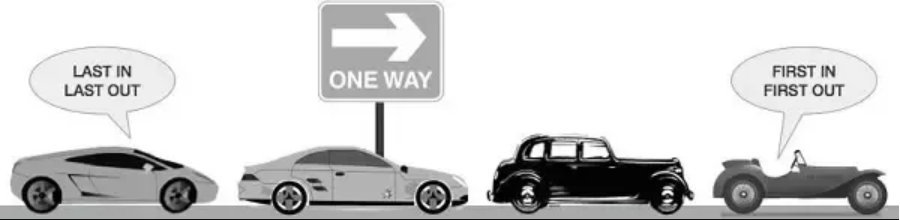
Single-Lane One-Way Road: First car go first

Ticket Counter: First person get ticket first and go out first
Some other Real Life Examples of Queue are
- Queue of processes in OS.
- Queue of people at any service point such as ticketing etc.
- Queue of packets in data communication.
- Queue of air planes waiting for landing instructions.
Application of Queue Data Structure in C
Queues are used for any situation where you want to efficiently maintain a First-in-first out order on some entities. Transport and operations research where various entities are stored and held to be processed later i.e the queue performs the function of a buffer.
In a multitasking operating system, the CPU cannot run all jobs at once, so jobs must be batched up and then scheduled according to some policy. Again, a queue might be a suitable option in this case.
Operation on a queue
The basic operation that can be perform on queue are;
- Insert an element in a queue.
- Delete an element from the queue.
LINKED LIST
Applications of linked list data structure
A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers as shown in the below image:
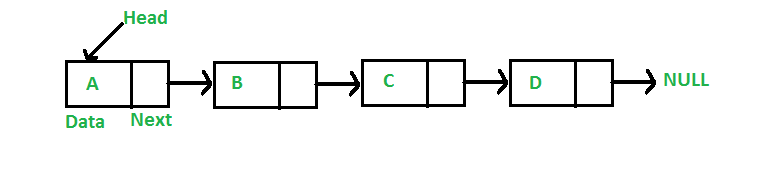
Applications of linked list in computer science –

Applications of linked list in computer science –
- Implementation of stacks and queues
- Implementation of graphs : Adjacency list representation of graphsis most popular which is uses linked list to store adjacent vertices.
- Dynamic memory allocation : We use linked list of free blocks.
- Maintaining directory of names
- Performing arithmetic operations on long integers
- Manipulation of polynomials by storing constants in the node of linked list
- representing sparse matrices
Applications of linked list in real world-
- Image viewer – Previous and next images are linked, hence can be accessed by next and previous button.
- Previous and next page in web browser – We can access previous and next url searched in web browser by pressing back and next button since, they are linked as linked list.
- Music Player – Songs in music player are linked to previous and next song. you can play songs either from starting or ending of the list.
TREES
Applications of tree data structure

Why Tree?
Unlike Array and Linked List, which are linear data structures, tree is hierarchical (or non-linear) data structure.
- One reason to use trees might be because you want to store information that naturally forms a hierarchy. For example, the file system on a computer:file system
———–/ <-- root / \ ... home / \ ugrad course / / | \ ... cs101 cs112 cs113 - If we organize keys in form of a tree (with some ordering e.g., BST), we can search for a given key in moderate time (quicker than Linked List and slower than arrays). Self-balancing search trees like AVL and Red-Black trees guarantee an upper bound of O(Logn) for search.
- We can insert/delete keys in moderate time (quicker than Arrays and slower than Unordered Linked Lists). Self-balancing search trees like AVLand Red-Black trees guarantee an upper bound of O(Logn) for insertion/deletion.
- Like Linked Lists and unlike Arrays, Pointer implementation of trees don’t have an upper limit on number of nodes as nodes are linked using pointers.
GRAPHS
Applications of Graph Data Structure
A graph is a non-linear data structure, which consists of vertices(or nodes) connected by edges(or arcs) where edges may be directed or undirected.
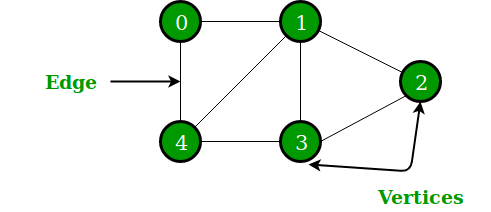

- In Computer science graphs are used to represent the flow of computation.
- Google maps uses graphs for building transportation systems, where intersection of two(or more) roads are considered to be a vertex and the road connecting two vertices is considered to be an edge, thus their navigation system is based on the algorithm to calculate the shortest path between two vertices.
- In Facebook, users are considered to be the vertices and if they are friends then there is an edge running between them. Facebook’s Friend suggestion algorithm uses graph theory.
- In Operating System, we come across the Resource Allocation Graph where each process and resources are considered to be vertices. Edges are drawn from resources to the allocated process, or from requesting process to the requested resource. If this leads to any formation of a cycle then a deadlock will occur.
Thus the development of algorithms to handle graphs is of major interest in the field of computer science.
Comments
Post a Comment